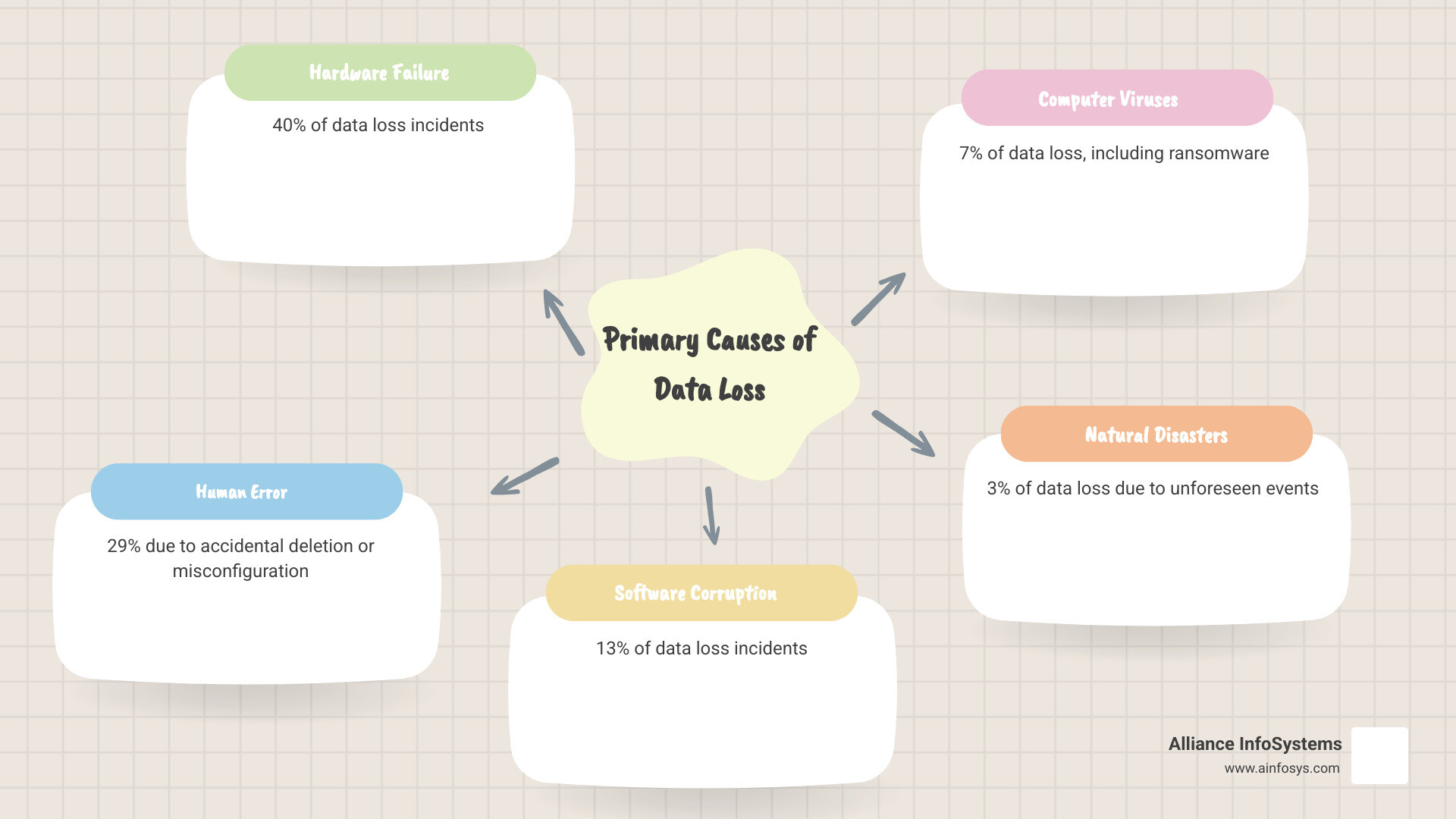
Why Your Business Can’t Afford to Ignore Server Backups
When server backup best practices are properly implemented, they become your business’s insurance policy against data disasters. Here are the essential practices every business needs:
Core Server Backup Best Practices:
- Follow the 3-2-1 rule: 3 copies of data, 2 different media types, 1 offsite location
- Automate your backups to eliminate human error and ensure consistency
- Test restores regularly – untested backups are worthless when disaster strikes
- Use multiple backup types: Full, incremental, and differential based on your needs
- Encrypt backup data both in transit and at rest for security
- Monitor backup jobs with alerts for failures and verification of success
- Document your strategy including Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
The statistics are sobering: 60% of backups are incomplete and 50% of restores fail. With threats like ransomware on the rise, a robust backup strategy is more critical than ever. According to the U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), ransomware continues to be a major threat to businesses, making secure backups essential.
Your servers hold the lifeblood of your business: customer data, financial records, and applications. When hardware fails, employees make mistakes, or cybercriminals strike, proper backups are often the only thing standing between business continuity and catastrophic loss.
Many businesses find their backup gaps only after a disaster. Something WILL eventually go wrong with your servers, making backup preparation not just smart, but essential for survival.
Building Your Foundation: Core Components of a Backup Strategy
Building server backup best practices is like constructing a house: you need a solid foundation and blueprints. Before choosing software or schedules, you must understand what you’re protecting and how quickly you need it back. This foundational work separates businesses that recover gracefully from those that scramble in panic.
Let’s walk through the essential building blocks for a rock-solid backup strategy custom to your business needs.
Defining Your Objectives: RPO and RTO
Two critical concepts drive every backup decision: Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). These measure how much data loss and downtime your business can tolerate.
Your Recovery Point Objective (RPO) answers: “How much data can we afford to lose?” For a busy e-commerce site, an RPO of 15 minutes might be critical. For an office with static documents, a 24-hour RPO could be acceptable.
Your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) answers: “How long can we be down before it causes serious damage?” A customer service operation might need an RTO of a few hours, while a research firm could handle a longer outage.
Reality check: 72% of businesses recovered from a backup at least once last year. Setting clear RPO and RTO targets isn’t just paperwork—it’s survival planning. To define these, assess data criticality across departments, identify revenue-generating systems, and understand compliance requirements. For more on building resilience, see our resources on Business Continuity.
Understanding Backup Types: Full, Incremental, and Differential
Different backup methods offer unique trade-offs.
A full backup copies everything selected, creating a complete snapshot. Restoration is fast and simple, as you only need one backup file. However, they consume significant storage and time.
Incremental backups copy only what’s changed since the last backup of any kind. They are fast and use minimal storage. The downside is complex restoration, requiring the last full backup plus every subsequent incremental backup in the correct order.
Differential backups copy everything that’s changed since the last full backup. Restoration is simpler than with incremental backups (requiring only the last full and the latest differential), but each differential backup grows larger over time.
| Backup Type | Backup Speed | Storage Usage | Restore Speed | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full | Slowest | Highest | Fastest | Lowest |
| Incremental | Fastest | Lowest | Slowest | Highest |
| Differential | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
The best strategy often combines all three, such as weekly full backups with daily incremental backups, to balance storage efficiency and recovery speed.
File-Level vs. Image-Level Backups
Deciding what to back up is as important as how often.
File-level backups focus on individual files and folders. They excel at granular recovery, allowing you to restore a single deleted file or corrupted database efficiently. However, they cannot quickly restore an entire server after a major failure.
Image-level backups create a complete snapshot of your entire server: OS, applications, settings, and data. This allows for a “bare-metal restore,” rebuilding your server on new hardware as if nothing happened. Image-level backups are your lifeline for disaster recovery scenarios like hardware failure or ransomware attacks, though they require more storage space.
A winning strategy combines both: file-level backups for daily protection and quick, granular restores, and image-level backups for major disasters. For guidance on building robust recovery plans, explore our expertise in Disaster Recovery.
The Ultimate Guide to Server Backup Best Practices
With a solid foundation, it’s time to implement the practical server backup best practices that protect your business. This is your playbook of proven strategies that separate businesses that recover quickly from those that don’t. These are battle-tested approaches that will make your backup strategy bulletproof.
The 3-2-1 Rule: The Gold Standard of Data Protection
The 3-2-1 backup rule is the gold standard for data protection. This simple framework is highly effective against catastrophic data loss.
- Keep three copies of your data: your original data plus two backups. Redundancy is key.
- Store copies on two different media types: for example, a local hard drive and a cloud service. This protects you if one storage type fails.
- Keep one copy offsite: this is your insurance against local disasters like fire, flood, or theft. Cloud storage is an excellent option for this.
A modern version, the 3-2-1-1-0 rule, adds one immutable backup (which can’t be altered, offering ransomware protection) and zero errors after testing.
Air-gapped backups provide even greater protection by keeping one copy completely disconnected from your network, making it immune to online threats.
Choosing Your Backup Destinations: Local, Offsite, and Cloud
Where you store backups is as important as how you create them. A smart strategy combines multiple storage types.
Local storage (external hard drive, NAS) offers speed and immediate access for quick restores. However, it’s vulnerable to the same local disasters as your primary data.
Offsite storage, like a secure facility or data center, protects you from local disasters. Recovery may be slower, but it ensures no single event can destroy all your data.
Cloud backup has revolutionized offsite storage, offering automatic, scalable, and secure data protection. Recovery speed depends on your internet connection, but it provides access from anywhere.
A hybrid strategy is often best, combining the speed of local storage for everyday issues with the disaster protection of the cloud for major emergencies. For more on cloud backup, see our guide to Data Backup solutions.
Automation and Monitoring: Essential Server Backup Best Practices
Automation is the key to a successful backup strategy, as it removes human error and ensures consistency.
- Schedule backups to run automatically at optimal times using tools like Windows Task Scheduler or cron jobs. The schedule should align with your data’s importance.
- Reduce human error, a leading cause of data loss. Automated systems follow the same process every time without fail.
- Verify backups automatically to ensure they are not corrupted and can be restored. This can include checksums or even automated test restores.
- Set up success and failure alerts via email or SMS to stay informed. You need to know immediately if a backup fails.
- Monitor logs to spot trends, optimize performance, and catch small issues before they become major problems.
Reliable server backup best practices depend on having tested, monitored, and automated backups you can count on when disaster strikes.
Advanced Strategies for Modern Data Protection
Basic backups are just the start. The digital world constantly evolves, and yesterday’s strategies may not protect you today. This section covers advanced tactics that create truly bulletproof server backup best practices.
The Critical Role of Testing in Your Backup Strategy
An untested backup is an unreliable backup. Industry data shows that 50% of restores fail, meaning half of businesses who think they’re protected find their backups are useless when needed most.
Regular disaster recovery testing is crucial. It validates your entire recovery process, confirming how long it takes to get critical systems online and ensuring your team knows their roles.
Sandbox restores are a key testing method. By restoring data to an isolated environment, you can verify that applications work and data is intact without affecting live systems.
For larger organizations, walkthrough tests (tabletop exercises) bring the team together to review the recovery plan step-by-step, identifying issues and building confidence.
The goal is to simulate real disaster scenarios regularly. By testing in advance, you’ll know what to expect and how long recovery will take. For more on why this matters, see 4 Important Disaster Recovery Statistics and Why They Matter.
Securing Your Backups: Encryption and Ransomware Resilience
Your backups are a primary target for cybercriminals. If they can corrupt your backups, they have all the leverage.
Data encryption is non-negotiable. Data must be encrypted both in-transit (as it moves across networks) and at-rest (when stored on devices). Encryption makes your data unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Access controls are your next line of defense. Enforce the principle of least privilege, granting users only the minimum permissions necessary. Multi-factor authentication should be mandatory.
Immutable storage is a powerful defense against ransomware. It creates backups that cannot be changed, deleted, or encrypted for a specified period. Even if ransomware strikes, these backups remain untouched.
The rising threat of ransomware makes these protections vital. Modern attacks actively hunt for and destroy backups. Secure backups mean you can restore your data without paying a ransom, which is your best defense against Data Loss.
Navigating Compliance and Retention Policies
Your backup strategy must align with legal and regulatory requirements.
Regulatory requirements like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS have strict rules for data protection, including secure backup procedures. Non-compliance can lead to massive fines.
Data retention policies must be precise. Keeping data too long increases storage costs and risks, while deleting it too soon can cause legal or operational problems. Your policy should define how long different types of data are kept.
Legal holds may require you to preserve specific data indefinitely, overriding normal retention schedules. Your backup system must be able to accommodate this.
Documentation is key. A documented strategy should detail what is backed up, how often, where it’s stored, and how it’s secured and tested. This proves you are taking data protection seriously. Also, understand the difference between backup (for fast recovery) and archiving (for long-term, low-cost retention) to build an efficient strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions about Server Backups
We’ve helped businesses protect their data for over 20 years and often hear the same questions. Here are answers to the most common concerns about server backup best practices.
What are the most common challenges in server backup?
The most common challenges are incomplete backups, often due to permission issues, network problems, or incorrect configuration. Other frequent issues include slow backup speeds that impact business operations, insufficient storage due to rapid data growth, and, most critically, failed restores. Half of all restore attempts fail, usually because of data corruption or a lack of testing.
A well-defined strategy with automation, monitoring, and regular testing can overcome most of these challenges.
How often should I back up my server?
This depends on your Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—how much data you can afford to lose.
- Mission-critical data that changes constantly (e.g., e-commerce transactions) may need backups every 15 minutes or even continuously.
- Regularly changing data (e.g., user files, emails) typically benefits from daily backups.
- Static or less critical data (e.g., archived projects) can often be backed up weekly or monthly.
The right frequency balances your tolerance for data loss against the cost and resources required for backups.
What is cloud-to-cloud backup?
Cloud-to-cloud backup means copying data from one cloud service (like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace) to a separate, independent cloud backup provider.
This is important because cloud providers operate on a shared responsibility model. They are responsible for their infrastructure’s uptime, but you are responsible for protecting your data from accidental deletion, user error, or ransomware attacks within your account.
Cloud-to-cloud backup creates an independent copy of your data, ensuring you can recover it even if something goes wrong within your primary cloud service. It’s a critical practice that aligns with the 3-2-1 rule, giving you an offsite copy in a separate location, even when your data lives entirely in the cloud.
Conclusion: Future-Proofing Your Backup Strategy
Implementing robust server backup best practices is your business’s lifeline in a crisis. We’ve seen how data loss—from hardware failure, human error, or ransomware—can devastate operations.
The path forward is clear. The 3-2-1 rule remains the gold standard. Automation eliminates human error, while regular testing transforms backups from hopeful wishes into reliable recovery tools. An untested backup is a gamble you can’t afford to take.
The digital landscape is constantly evolving. Data volumes are exploding, and cyber threats are growing more sophisticated. Your backup strategy cannot be a “set it and forget it” plan; it must be a living process that receives regular attention.
Security must be woven into every aspect of your plan, with encryption, access controls, and immutable storage as essential defenses. Compliance requirements add another layer, demanding documented retention policies and proven recovery capabilities.
The statistics are clear: with many backups incomplete and restores failing, the margin for error is thin. Businesses that implement comprehensive server backup best practices are the ones that survive data disasters.
At Alliance InfoSystems, we’ve spent over 20 years helping Maryland businesses steer these exact challenges. Since our founding in 2004, we’ve seen how proper backup strategies separate thriving companies from those that struggle to recover from data disasters. Our flexible, customized approach means your backup solution fits your specific needs, not some one-size-fits-all template.
Don’t wait for a disaster to test your backup strategy. The time to act is now, while your data is safe and your systems are running smoothly. Develop a robust data backup and recovery plan with our expert services and transform your backup strategy from a source of worry into a foundation of confidence.