Why Virtual Desktop Servers Matter for Modern Businesses
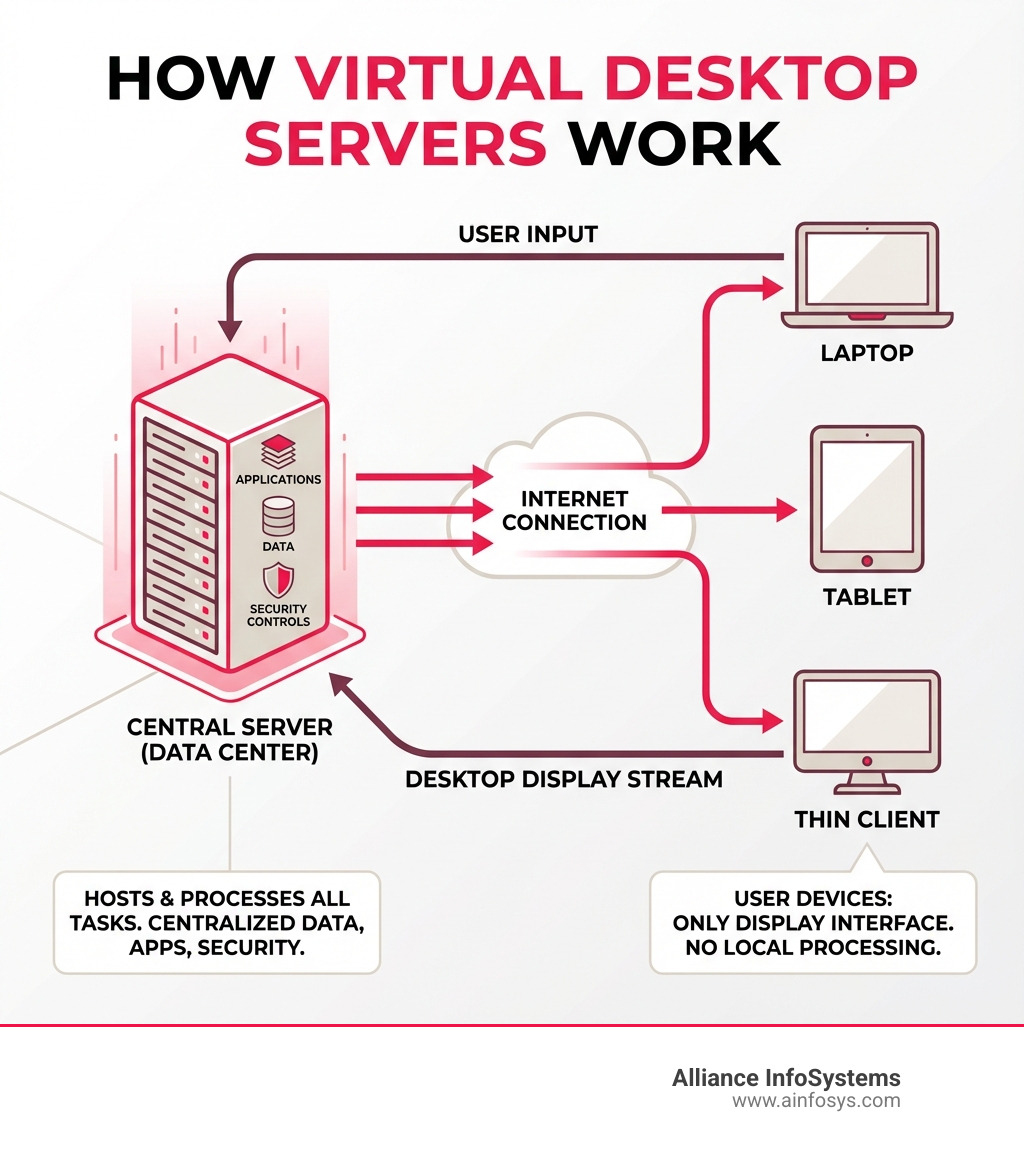
Virtual desktop servers are centralized systems that host desktop operating systems and applications, allowing users to access their work environment remotely from any device. Instead of running on local computers, all processing happens on powerful servers, with the user’s device simply displaying the streamed desktop.
Key characteristics of virtual desktop servers:
- Centralized hosting – Desktops run on servers in a data center or cloud.
- Remote access – Users connect from laptops, tablets, or thin clients.
- Managed infrastructure – IT controls security, updates, and apps from one location.
- Flexible delivery – Provides full desktops or just specific applications.
- Scalable resources – Easily add or remove users without new hardware.
The global virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) market is projected to reach $35.7 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 14.5%, while the Desktop as a Service (DaaS) market is expanding at 15.2% annually.
For modern businesses, this technology solves real problems. It eliminates the need for expensive computers for every employee, enables secure work from anywhere, and protects sensitive data even if a device is lost or stolen.
However, choosing the right solution—VDI or DaaS, on-premise or cloud—involves weighing factors like cost, security, and scalability. This guide provides a practical checklist to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Virtual Desktops
Before comparing solutions, let’s clarify what virtual desktops are and how they operate. Think of them as your digital workspace, available anywhere and powered by robust infrastructure like the servers you see below.
What is a Virtual Desktop and How Does It Work?
A virtual desktop is a workstation that exists on a centralized server rather than a physical machine. Your entire computer—OS, apps, and files—lives in a data center or the cloud. The server does all the heavy lifting, while your local device simply acts as a display.
Here’s how it works:
- Hosting: Virtual desktops are hosted on powerful servers, created from a master “OS image” containing the operating system and applications for consistency.
- Connection: Users connect from any device using a client app or web browser, establishing a secure link to the server.
- Streaming: The server processes all tasks and streams the desktop’s visual output to the user’s device. The user’s inputs are sent back, creating a responsive experience that feels like a local PC.
This allows you to access a full desktop from anywhere, on almost any device, with all data securely managed centrally.
Virtual Desktop vs. Virtual Machine (VM): What’s the Difference?
While related, a virtual desktop and a virtual machine (VM) are not the same. A VM is the foundational technology—a software-based emulation of a physical computer. A virtual desktop is the user-facing application that uses a VM to deliver a complete desktop experience.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Virtual Machine (VM): The Foundation
- A file that acts like a physical computer with its own virtual hardware (CPU, RAM, storage).
- Hosts an operating system (e.g., Windows Server, Linux).
- Can be used for many purposes, like hosting servers or databases.
- Virtual Desktop: The User’s Workspace
- Is created by VMs to deliver a personalized desktop environment.
- Stores workspace elements (OS, user profiles, apps) on a central server.
- Focuses on providing an interactive, graphical interface for user productivity.
In short, every virtual desktop relies on a VM, but not every VM is a virtual desktop. For a deeper dive, read our article: What’s the difference between virtual servers and virtual desktops?.
Key Benefits: Boosting Productivity and Security
Businesses are turning to virtual desktop servers for compelling reasons:
- Improved Security: This is a top driver. Sensitive data remains in the data center, not on endpoint devices. If a laptop is lost or stolen, no data is compromised. Centralized security policies, backups, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are easier to enforce, helping with compliance. For more on this, see our Virtual Security Operations Center Guide.
- Increased Productivity & Remote Workforce Enablement: Employees can access their familiar desktop and applications from any location, on any device. This flexibility is essential for remote/hybrid work and supports “Bring Your Own Device” (BYOD) policies while maintaining IT control.
- Simplified IT Management: Instead of managing hundreds of physical machines, IT teams manage a single “golden image.” Updates and patches are rolled out once, drastically reducing maintenance time and effort.
- Cost Savings: Virtual desktops can lead to long-term savings by extending the life of older hardware (which can be used as thin clients), reducing power consumption, and optimizing software licensing. Multi-session capabilities, like in Azure Virtual Desktop, allow multiple users to share one VM, cutting operational costs. For example, Eurowings reduced operating costs by over 50% with this technology.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: With data and apps centrally stored and backed up, recovering from hardware failure or a disaster is much faster. Users can quickly connect to a new desktop instance, minimizing downtime.
Types of Virtual Desktop Solutions
Virtual desktop servers are deployed in two primary models: Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Desktop as a Service (DaaS). Understanding their differences is key to choosing the right fit for your organization.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
VDI involves hosting desktop operating systems on centralized servers that your organization owns and manages, typically in your own data center.
Key characteristics of VDI:
- Full Desktop Environment: VDI delivers a complete, personalized desktop experience to each user.
- Persistent vs. Non-Persistent Desktops:
- Persistent VDI: Users get a dedicated virtual desktop that saves all changes, offering a highly personalized experience for power users.
- Non-Persistent VDI: Users get a standardized desktop that resets after each session, which is cost-effective and ideal for task workers.
- High Customization and IT Control: VDI offers maximum control over hardware, security, and applications, which is ideal for organizations with strict compliance or unique software needs.
- Deployment Flexibility: VDI can be deployed on-premises or in a private cloud, giving you direct control over the infrastructure.
For businesses that require granular control and want to leverage existing IT infrastructure, VDI is a powerful solution. You can learn more in our Remote Desktop Services overview.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
DaaS is a cloud-based solution where a third-party provider hosts and manages the virtual desktop infrastructure for you. You subscribe to the service and access desktops over the internet. The DaaS market is growing rapidly, with a projected CAGR of 15.2% from 2024 to 2030.
Key characteristics of DaaS:
- Subscription Model: DaaS operates on a subscription fee (typically per user, per month), shifting costs from capital to operational expenditure (OpEx).
- Managed Provider: The provider handles all infrastructure management, including maintenance, updates, and security, freeing up your IT team.
- Reduced Management Overhead: With DaaS, you don’t worry about managing hardware or hypervisors; the provider handles it all.
- Scalability: DaaS solutions are highly scalable, allowing you to add or remove users in minutes to match business needs.
- Accessibility: Users can securely access their desktops from any device with an internet connection, making it perfect for remote and global teams.
DaaS is an excellent choice for businesses seeking flexibility, predictable costs, and a reduced IT burden without a large upfront investment.
Comparing VDI and DaaS
This table summarizes the key differences between VDI and DaaS:
| Criteria | Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) | Desktop as a Service (DaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | High. Your IT team manages all aspects of the infrastructure, operating systems, and applications. | Lower. The provider manages the underlying infrastructure; your IT team manages the virtual desktops, applications, and user access. |
| Cost Model | Capital Expenditure (CapEx) for hardware and software licenses, plus ongoing Operational Expenditure (OpEx) for maintenance and staffing. | Operational Expenditure (OpEx) through subscription fees, typically per user per month/hour. Minimal upfront hardware investment. |
| Scalability | Scalability is managed internally. Requires planning and investment in additional hardware/software. | Highly scalable. Easily add or remove users and resources on demand, often within minutes. |
| Management | High IT burden. Requires dedicated staff with VDI expertise to manage the entire stack. | Lower IT burden. Provider handles infrastructure maintenance, patching, and updates. |
| Ideal Use Case | Large enterprises with strict compliance, unique customization needs, existing data centers, and IT resources. | Small to medium businesses, organizations with fluctuating user numbers, remote workforces, and those seeking to reduce IT overhead and upfront costs. |
Choosing between VDI and DaaS depends on your organization’s size, budget, IT resources, and desired level of control.
Your Checklist for Choosing the Right Virtual Desktop Servers
Selecting the right virtual desktop servers solution requires a careful look at your unique operational needs. This checklist will guide you through the key factors to consider.
Assessing Your Use Case and Performance Needs
First, understand who will use the virtual desktops and what they will do. This determines the performance requirements.
- Full Desktop vs. Application Access: Do users need a full desktop, or just access to specific applications? For some, application virtualization may be more cost-effective than a full VDI solution.
- User Profiles and Workloads:
- Task Workers: Perform repetitive tasks with a few apps (e.g., call centers). They are good candidates for non-persistent VDI or DaaS.
- Knowledge Workers: Use a range of office apps (e.g., Microsoft 365). They benefit from persistent desktops with moderate resources.
- Power Users/Developers: Need high performance for specialized software (e.g., CAD, coding). They require robust virtual desktops, possibly with dedicated GPUs.
- Graphics-Intensive Workloads: Users working with 3D modeling or high-resolution video will need virtual desktops with virtualized GPUs for smooth performance.
Key questions to ask about user requirements:
- What applications are essential for your users?
- Do any users require specialized hardware (e.g., multiple monitors, GPUs)?
- What are the peak usage times for your workforce?
- How important is a personalized desktop experience?
Understanding these needs helps tailor a solution that ensures a great user experience without overspending.
Analyzing Cost: TCO and Pricing Models
Cost is a major factor, but it’s crucial to look beyond the initial price to the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): This includes all upfront and ongoing expenses.
- VDI: Involves Capital Expenditure (CapEx) for servers, storage, and licenses, plus Operational Expenditure (OpEx) for power, cooling, and IT staff.
- DaaS: Primarily OpEx through subscription fees that cover infrastructure, management, and support, with minimal CapEx.
- Licensing Costs: This can be complex. You’ll need licenses for the OS (e.g., Windows 10/11), applications, and the virtualization platform. Cloud providers may bundle licenses or allow you to bring your own. For instance, Azure Virtual Desktop’s multi-session Windows 11 capability can significantly reduce licensing and compute costs.
- Pricing Models: DaaS often uses a flexible pay-per-use model, while VDI typically involves larger upfront investments.
A thorough Cloud Virtualization Guide 2025 can offer more insights into financial planning. The goal is to find the best value that supports your business objectives.
Evaluating Security and Compliance
Security is paramount, and virtual desktops offer significant advantages if configured correctly.
- Data Sovereignty: Know where your data is stored. Some regulations require data to remain within specific geographic boundaries, which can be addressed with self-hosted solutions or specific cloud regions.
- Centralized Security Policies: Virtual desktops allow you to enforce security policies centrally, controlling user access, implementing strong passwords, and pushing updates simultaneously. This reduces the attack surface compared to managing individual PCs.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Any robust solution must support MFA for an added layer of security.
- Compliance Certifications: If you must comply with regulations like HIPAA or PCI DSS, ensure your chosen solution has the necessary certifications. Many major providers hold over 100 compliance certifications. You can learn more about compliance certifications to see what applies to your industry.
- Data Encryption: Ensure data is encrypted both in transit (as it’s streamed) and at rest (on the server).
Planning for Scalability and Management
Your IT infrastructure should adapt as your business grows, while remaining manageable for your IT team.
- Scalability on Demand: Can you easily add or remove users? DaaS solutions excel here, offering near-instant scalability. For VDI, this requires planning for growth. The VDI market’s projected growth to $35.7 billion by 2032 highlights the demand for scalable solutions.
- Management Tools and Automation: Look for solutions with intuitive management consoles and automation for tasks like:
- Image Management: Easily creating, updating, and deploying desktop images.
- User Provisioning: Quickly setting up new users.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics: Tools to monitor performance and troubleshoot issues.
- Hybrid Cloud Capabilities: A hybrid approach, combining on-premises and cloud resources, can be ideal for balancing control and scalability.
Partnering with a provider experienced in Managed IT Services can be invaluable. We can help design, implement, and manage your virtual desktop environment, allowing your team to focus on core business functions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Virtual Desktop Technology
We often encounter common questions when discussing virtual desktop servers with our clients. Let’s address some of the most frequent ones.
How do virtual desktop servers handle software licensing?
Software licensing in a virtual desktop environment can be a bit more nuanced than with traditional physical desktops. Generally:
- Centralized Management: Licenses for the operating system and applications are managed centrally. This simplifies compliance tracking and often allows for more efficient license utilization, as licenses can be dynamically assigned to users or pooled.
- Provider-Specific Requirements: Different virtual desktop providers (whether DaaS or VDI) have specific licensing requirements or bundles. For example, to access Windows 11 and Windows 10 client OS capabilities with Azure Virtual Desktop, users typically need specific Microsoft 365 or Windows Enterprise licenses. For server workloads, Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Client Access Licenses (CALs) with active Software Assurance are often required.
- Verification is Crucial: It’s absolutely critical to verify your existing licenses’ eligibility and understand the licensing model of your chosen virtual desktop solution to avoid compliance issues and unexpected costs. Some providers allow “bring your own license” (BYOL), while others include licenses in their subscription fees. Always consult with your provider or a licensing expert to ensure full compliance.
What kind of internet connection is needed for a good user experience?
The quality of the internet connection is paramount for a smooth virtual desktop experience. After all, you’re streaming your entire desktop!
- Stable, Low-Latency, High-Bandwidth: A stable connection with low latency (minimal delay) and sufficient bandwidth (data transfer speed) is recommended. Choppy performance is often a sign of an inadequate network connection.
- Workload-Dependent Requirements: The exact requirements depend heavily on what users are doing:
- Basic Office Tasks (email, word processing): Relatively low bandwidth, but stability and low latency are still important.
- Video Conferencing/Streaming: Requires more consistent bandwidth (e.g., 5-10 Mbps per user) and very low latency.
- Graphics-Intensive Applications (CAD, video editing, 3D modeling): Demands significantly higher bandwidth (20+ Mbps per user) and extremely low latency to avoid noticeable lag.
- Optimizing the Connection: We always recommend wiring your computer directly to your router with an Ethernet cable if possible, especially for demanding tasks. If Wi-Fi is necessary, use a modern router (802.11 AC or AX) and connect to the 5 GHz band for better speed and less interference. Many modern virtual desktop solutions also employ sophisticated display protocols (like RDP, PCoIP, HDX) that optimize performance over variable network conditions, compressing data and adapting to available bandwidth to provide the best possible experience.
Can you use multiple monitors with a virtual desktop?
Yes, absolutely! Most modern virtual desktop solutions are designed to support multi-monitor setups, allowing users to replicate their physical office environment and boost productivity.
- Client Software and Hardware Support: The ability to use multiple monitors depends on two main factors:
- The virtual desktop client software: The client application you use to connect to your virtual desktop must support multi-monitor configurations. Most leading solutions do.
- The user’s endpoint hardware: Your local device (laptop, thin client, etc.) and its graphics card must be capable of driving multiple displays.
- Improved Productivity: For many professionals, having multiple screens is essential for multitasking and efficiency. Virtual desktops make this possible, providing the flexibility to spread applications across several displays, just as you would with a traditional PC. This means you can have your email on one screen, a document on another, and a web browser on a third, all seamlessly delivered from your virtual environment.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of virtual desktop servers can feel like a complex journey, but with the right checklist and understanding, it becomes a strategic decision to empower your business. We’ve seen that choosing the right solution requires a careful evaluation of many factors: your specific use cases, performance needs, cost considerations (including TCO and licensing), ironclad security requirements, compliance mandates, and your plans for scalability and ongoing management.
Whether you lean towards the granular control of VDI or the agile, managed convenience of DaaS, the goal remains the same: to create a flexible, secure, and productive work environment for your team. This technology is not just a trend; it’s a foundational shift in how businesses operate, offering unparalleled advantages in today’s remote and hybrid work era.
Here at Alliance InfoSystems, we understand the intricacies of virtual desktop technology and the unique needs of businesses in Maryland. With over 20 years of experience, we pride ourselves on offering flexible, customized, and cost-efficient services designed to simplify your IT infrastructure.
Don’t let the complexity deter you. Partnering with an experienced IT provider like us can simplify the entire process, from initial assessment and solution design to implementation and ongoing management, ensuring a seamless transition and sustained success.
Explore more about Virtual Desktops and let us help you transform your workspace. Get expert help with your cloud virtualization strategy today!