The Stakes Are Higher Than You Think: Why Server Backup Best Practices Matter
Server backup best practices are your business’s lifeline when disaster strikes. With statistics showing that 60% of backups are incomplete and 50% of restores fail, a solid backup strategy isn’t just recommended—it’s essential for survival.
Essential Server Backup Best Practices:
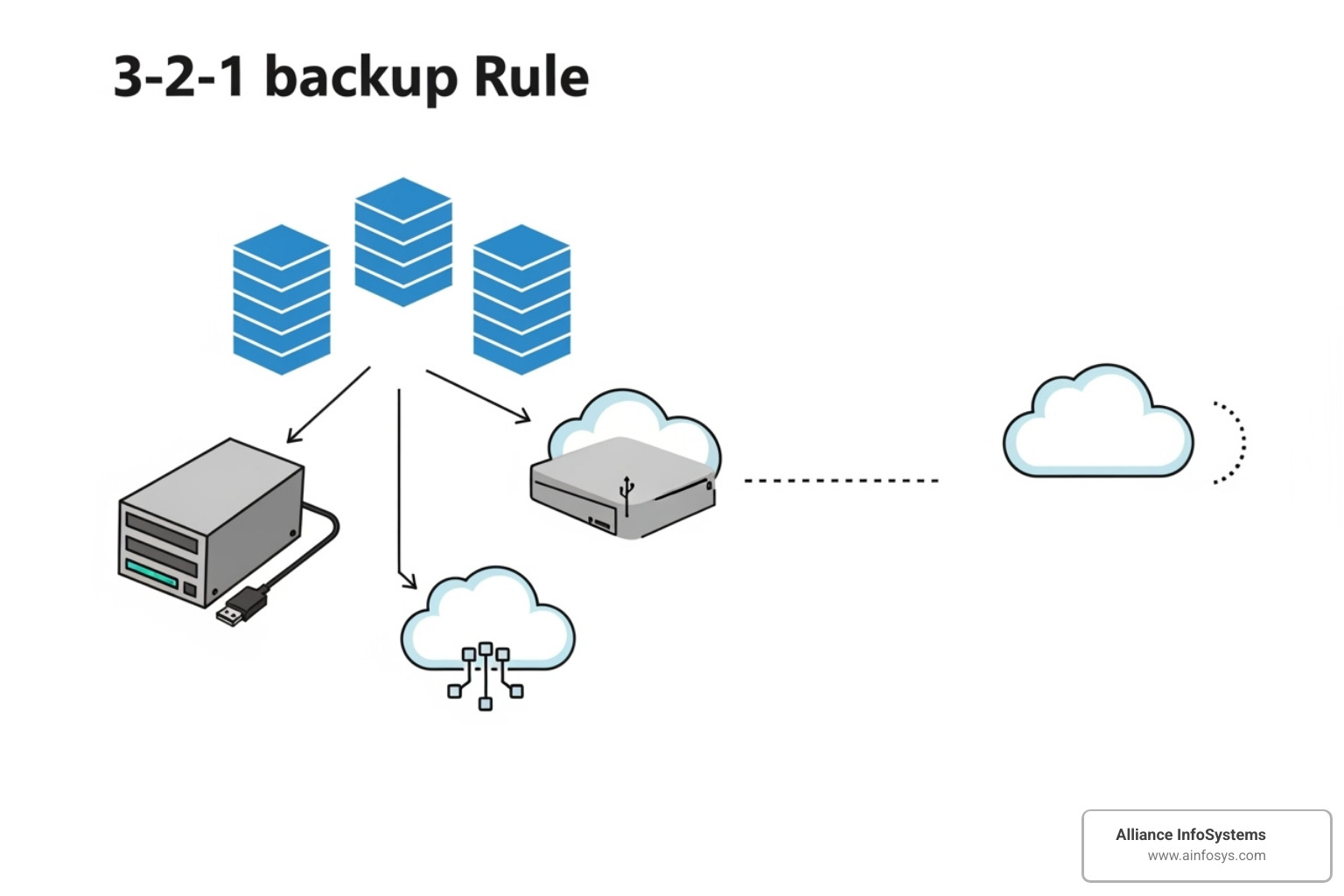
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Keep 3 copies of data, on 2 different media types, with 1 copy stored offsite
- Test Regularly: Perform restore tests monthly to verify backup integrity
- Automate Everything: Schedule automatic backups to eliminate human error
- Define Clear Objectives: Set Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
- Encrypt All Data: Protect backups both in transit and at rest
- Monitor Daily: Check backup status reports and address failures immediately
The numbers paint a stark picture: 93% of companies that lose data for more than 10 days file for bankruptcy within a year. Meanwhile, backup failures cause an average of 79 minutes of downtime, costing businesses roughly $84,650 per hour.
Roughly 40% of small and medium-sized businesses will be attacked by cybercriminals within a year, and 61% of all SMBs have already been attacked. When ransomware strikes or hardware fails, your backup strategy becomes the difference between a minor inconvenience and a business-ending catastrophe.
The reality is sobering: only 30% of IT leaders have a fully documented disaster recovery strategy. This gap creates massive vulnerability for businesses of all sizes.
The Stakes Are High: Why a Solid Server Backup Strategy is Non-Negotiable
Your business data is everything. Those customer records, financial files, and years of hard work sitting on your servers are the foundation of your entire operation. When that data disappears—whether from a ransomware attack, hardware failure, or human error—the consequences can be devastating.
The harsh reality is that data loss can kill a business. We’re not being dramatic: 93% of companies that lose data for more than 10 days file for bankruptcy within a year. That’s a sobering statistic that should make every business owner take notice.
Business continuity planning isn’t just about having backups; it’s about ensuring your company survives when disaster strikes. Without proper server backup best practices in place, you could face weeks of downtime, angry customers, and crippling financial losses.
The threat landscape is particularly scary for smaller businesses. 61% of all SMBs have already been attacked, as cybercriminals target companies they perceive as having weaker defenses. Your backup strategy isn’t just an IT consideration—it’s a critical business survival tool. For more insights on protecting your business, check out our Cybersecurity resources.
Compliance requirements add another layer of complexity. Depending on your industry, losing certain types of data could result in hefty fines and legal troubles on top of operational disruptions.
Common Backup and Recovery Pitfalls
Most businesses think they’re protected, but the statistics are eye-opening: 60% of backups are incomplete and 50% of restores fail. This means there’s a coin-flip chance your backup won’t work when you need it most.
- Incomplete backups are common. Software might miss a critical database or fail to capture recent changes, leaving you with a backup that appears successful but is missing key components.
- Restore failures are also common, often because organizations create backups without ever testing the recovery process. You might have perfect backup files, but the restoration itself fails when you need it most.
- Many IT teams underestimate recovery time dramatically, assuming a restore will take hours when it could take days or weeks.
- The most dangerous pitfall is a lack of a documented plan. Shockingly, only 30 percent of IT leaders report having a fully documented disaster recovery strategy. When crisis hits, teams waste precious time figuring out what to do instead of executing a well-rehearsed plan.
The Critical Role of Regular Testing
An untested backup is just expensive storage. Without regular testing, you’re simply hoping your backups will work when disaster strikes.
Regular testing allows you to:
- Verify backup integrity to ensure files aren’t corrupted and contain the data you expect.
- Ensure recoverability by performing actual restore operations to confirm systems can be rebuilt and function normally.
- Identify gaps in your strategy, such as critical files that aren’t being backed up or a restore process that takes longer than anticipated.
- Simulate disaster scenarios to help your team practice under pressure and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Understand restore time, which is crucial for business planning and managing expectations during an emergency.
Regular testing transforms your backup strategy from a hopeful insurance policy into a reliable business continuity tool.
Building a Bulletproof Strategy: Core Server Backup Best Practices
Building a robust server backup strategy is like constructing a fortress for your data. It requires careful planning, automation, monitoring, and regular reviews to remain effective.
The foundation starts with taking inventory of your entire IT environment: physical servers, virtual machines, databases, applications, and individual files. The best server backup best practices focus on knowing what data matters most, automating the process to eliminate human error, monitoring everything continuously, and reviewing your strategy regularly.
The 3-2-1 Rule: A Cornerstone of Server Backup Best Practices
The 3-2-1 rule is a simple, time-tested approach that has saved countless businesses from disaster.
- Three copies of your data means you have your original data plus two separate backups.
- Two different media types protects you from device-specific failures. One copy might be on a server’s internal storage, another on a Network Attached Storage (NAS), and the third in the cloud.
- One copy stored offsite is your insurance against local disasters like fires, floods, or theft. When these things happen, your offsite backup becomes your lifeline.
This approach creates both redundancy and diversity, ensuring you have options even if one backup method fails. For more details on implementing this strategy, check out The 3-2-1 backup rule explained. At Alliance InfoSystems, we’ve seen how Professional Data Backup Solutions Essential for Business operations, especially when built on solid principles like the 3-2-1 rule.
Defining Your RPO and RTO
Two critical acronyms define your backup strategy: Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO).
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) answers the question: “How much data can we afford to lose?” An RPO of one hour means you need backups running at least hourly.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) tackles a different question: “How long can we be down before it impacts the business?” An RTO of four hours means your recovery process must be completed within that timeframe.
Not all data is created equal. Mission-critical systems that directly impact revenue need low RPOs and RTOs, while less critical data can tolerate daily backups and longer recovery times. Getting these numbers right ensures your most important systems get the protection they deserve without over-spending on low-priority data.
Creating and Managing Retention Policies
Deciding how long to keep backups is a critical decision, especially with the threat of ransomware.
Versioning is your secret weapon against ransomware. If you only keep one backup copy, it might already be infected by the time you find an attack. Versioning means keeping multiple snapshots of your data from different points in time (hourly, daily, weekly), allowing you to roll back to a clean version from before the infection started.
Retention schedules balance cost with necessity. Financial records might need to be kept for seven years due to regulations, while operational data may only need a few weeks of storage. The Grandfather-Father-Son (GFS) approach is a popular method for structuring this.
Yes, keeping more versions means higher storage costs. But the cost of not having the right data when you need it—whether for compliance, audits, or cyber recovery—almost always dwarfs the storage expense. Our guide on Data Recovery 101: What to do when disaster strikes can help you steer the recovery process effectively.
Choosing Your Tools: Backup Types, Technologies, and Storage
Choosing backup tools is like building a toolbox; you need the right tool for each job. A comprehensive defense system combines different backup types, storage locations, and security measures.
Modern server backup best practices emphasize automation because it eliminates human error, runs consistently, and frees up your IT team. Think of it as a reliable assistant who never forgets to do their job.
| Backup Type | Speed | Storage Usage | Restore Complexity | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Slow | High | Low (single set) | Initial baseline, infrequent critical data |
| Incremental | Fast | Low | High (full + all increments) | Frequent backups of rapidly changing data |
| Differential | Medium | Medium | Medium (full + latest differential) | Balanced approach, quicker restores than incremental |
File vs. Image Backups: What’s the Difference?
File-level and image-level backups serve very different purposes. Knowing the difference is key to a complete data protection strategy.
File-level backups selectively copy individual files and folders. They are perfect for recovering accidentally deleted documents, as their granular restore capability lets you grab exactly what you need.
Image-level backups are for disaster recovery. They take a complete snapshot of your entire system: operating system, applications, settings, and data. This bare-metal recovery capability lets you restore an entire server to new hardware, getting your business back online quickly after a major disaster.
The smart approach is to use both. File backups handle small incidents, while image backups prepare you for major catastrophes.
Local, Offsite, and Cloud Storage Options
Where you store your backups is as important as how you create them. A hybrid approach is often best.
Local storage, like external drives or Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices, offers speed and immediate access for quick restores. However, local storage is vulnerable to the same physical disasters that could affect your main systems.
This is where offsite and cloud storage become essential. Cloud storage protects against physical disasters, offers unlimited scalability, and provides access from anywhere. You can explore more about this evolution in Cloud Computing Trends. The cloud isn’t magic, though; you still share responsibility for your data’s security, as outlined in the cloud shared responsibility model.
A hybrid approach combining local and cloud storage aligns with the 3-2-1 rule, giving you the speed of local recovery and the resilience of offsite copies.
Don’t forget cloud-to-cloud backup for services like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace. These providers don’t typically protect against user-deleted data or ransomware, so a separate backup ensures you maintain control.
Securing Your Backups: The Last Line of Defense
Your backups are your last line of defense against data loss, so securing them is critical.
Data encryption is essential. Your backups must be encrypted both in-transit (while being sent to storage) and at-rest (while stored). Encryption scrambles your data, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Immutable backups provide powerful protection against ransomware. These are backup copies that cannot be altered or deleted for a specified period, ensuring a clean recovery point.
Access controls ensure only authorized personnel can reach your backup systems. Implement strict permissions based on the principle of least privilege and use multi-factor authentication to add another layer of security.
Consider this sobering fact: in 30% of ransomware attacks, data is not only encrypted but also stolen. Secure backups protect against both data loss and data theft, making them doubly important for your business’s survival.
Frequently Asked Questions about Server Backup Best Practices
We get a lot of questions from businesses trying to steer the complex world of server backups. Here are the most common ones.
How often should our server backup strategy be reviewed?
Backup strategies aren’t static; they must evolve as server backup best practices change. What worked last year might leave you vulnerable today.
We recommend reviewing your strategy at least annually, or more frequently for highly regulated industries or businesses experiencing rapid growth. These changes can dramatically affect your backup needs.
As a simple rule, revisit your backup strategy whenever your IT environment or business operations change significantly. New software, data volumes, or compliance requirements all warrant a review.
What are the key features to look for in a server backup solution?
When choosing a backup solution, several key features separate a good system from a great one.
- Automation is at the top of the list. Manual backups are prone to human error.
- Support for various backup types (full, incremental, differential, and image-level) provides flexibility.
- Flexible storage options (local, cloud, hybrid) are crucial for implementing the 3-2-1 rule.
- Robust reporting and monitoring provide real-time alerts and detailed logs.
- Strong encryption for data both in transit and at rest is non-negotiable.
- Reliable technical support is essential when disaster strikes.
What are the main challenges IT teams face with server backups?
IT teams consistently struggle with several common backup challenges.
- Managing storage space and slow backup speeds is a constant resource puzzle. This can be addressed with smarter strategies like incremental backups and data deduplication.
- Ensuring backup completeness and integrity is surprisingly difficult. This often stems from a lack of proper monitoring or over-reliance on manual processes.
- The complexity of testing overwhelms many IT departments. Skipping tests is like buying insurance but never checking the policy coverage.
- Human error still causes many backup failures. Automation, training, and clear procedures are the best defense.
- Evolving threats like ransomware require modern solutions like immutable backups and air-gapped storage.
The good news is that these challenges are solvable with the right approach, tools, and expert partnership.
Secure Your Business Future with a Proactive Backup Strategy
Your data isn’t just files on a server – it’s the heartbeat of your business. Every customer record, financial transaction, and creative project represents hours of work and thousands of dollars in value. When you accept server backup best practices, you’re doing something powerful: changing what could be your biggest vulnerability into your strongest competitive advantage.
Think about it this way. While your competitors scramble to recover from data disasters, your business keeps running smoothly. While they lose customer trust and revenue, you maintain operations and actually gain market share. That’s the power of proactive data protection – it turns crisis into opportunity.
The reality is that business resilience isn’t built overnight. It’s crafted through careful planning, smart technology choices, and the wisdom that comes from experience. Every backup you create, every test you run, and every policy you implement builds a stronger foundation for your company’s future.
We’ve seen how the right backup strategy can save businesses from catastrophic loss. Over our 20 years serving Maryland businesses, we’ve helped companies bounce back from ransomware attacks, hardware failures, and natural disasters. The ones who invested in robust backup systems beforehand? They barely missed a beat. The ones who didn’t? Well, let’s just say some stories don’t have happy endings.
At Alliance InfoSystems, we understand that every business is different. Your backup needs aren’t the same as the company down the street. That’s why we take time to understand your operations, your data, and your goals before designing a protection strategy. We believe in flexible, customized solutions that grow with your business – not one-size-fits-all approaches that leave gaps in your defense.
The best part? You don’t have to become a backup expert overnight. Our team brings over two decades of experience to the table, handling the complex technical details while you focus on running your business. We make data protection simple, reliable, and surprisingly affordable.
Ready to stop worrying about data loss? Let’s develop a robust strategy with our Data Backup and Recovery services. Together, we’ll build the kind of bulletproof backup system that lets you sleep soundly, knowing your business is protected no matter what tomorrow brings.