Why Compliance for Healthcare is the Cornerstone of Patient Safety and Organizational Integrity
Compliance for healthcare is the practice of adhering to the laws, regulations, and ethical standards governing healthcare operations. At its core, it exists to prevent fraud, safeguard patient privacy, and ensure the highest standards of safety and quality in medical services.
If you’re searching for what healthcare compliance means for your organization, here are the essentials:
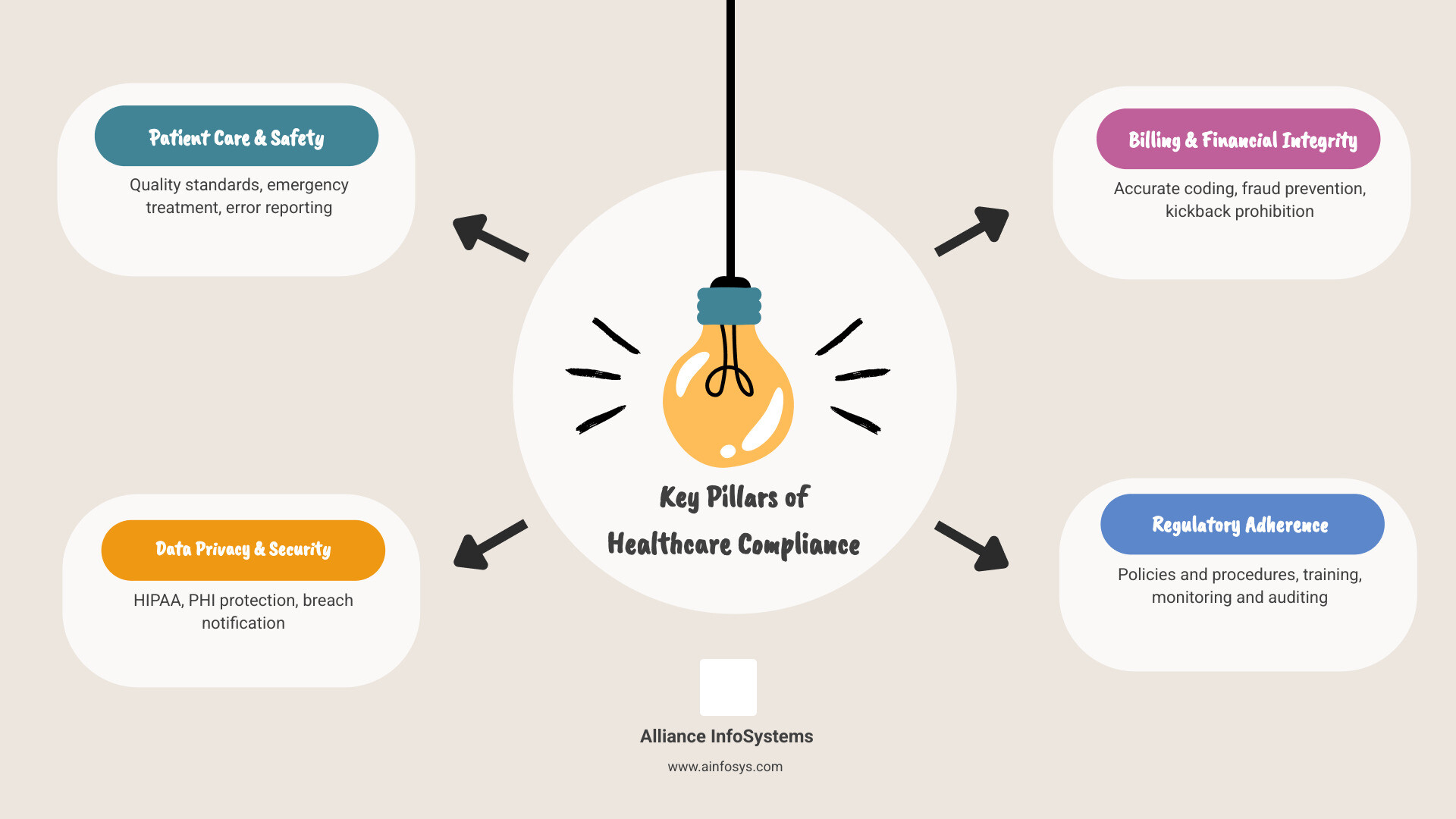
- Patient Privacy & Data Security: Protect sensitive health information through HIPAA and HITECH Act requirements
- Financial Integrity: Prevent fraud and ensure ethical billing practices via laws like the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute
- Patient Safety: Maintain quality care standards through regulations like EMTALA and PSQIA
- Operational Standards: Implement policies, training, and monitoring systems to maintain adherence
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Face fines ranging from $137 to over $68,928 per HIPAA violation, up to $1 million for Sunshine Act violations, and potential exclusion from federal programs
In a multitrillion-dollar industry where decisions impact human lives, this regulatory framework is critical. The stakes are high for patients who trust providers with their well-being and for organizations that face severe consequences when compliance fails. While navigating this complex landscape can feel overwhelming, especially for smaller providers, non-compliance is not an option. By understanding key regulations and building a strong compliance program, organizations can protect their patients, reputation, and bottom line.
What is Healthcare Compliance and Why is It Crucial?
Think of compliance for healthcare as the foundation upon which patient trust is built. It’s not about paperwork; it’s about protecting people, ensuring they receive safe care, and keeping their private information secure. In a multitrillion-dollar global industry, compliance provides the ethical framework to prevent errors, system failures, and fraud.
A strong compliance program delivers multiple benefits:
- Patient Safety & Rights: High standards for treatment and data protection lead to better, safer care.
- Reduced Legal Risk: Following the rules proactively protects against investigations, lawsuits, and regulatory actions. Effective Risk Management in Healthcare IT is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities early.
- Trust & Reputation: A solid compliance record signals integrity to patients, partners, and the community.
- Operational Efficiency: Clear policies and standardized procedures reduce errors and help staff perform more effectively.
- Financial Health: While compliance requires investment, it prevents the catastrophic costs of violations and ensures proper billing and reimbursement.
The High Cost of Non-Compliance
The penalties for compliance for healthcare failures can be devastating. HIPAA violations can result in fines from $137 to over $68,928 per violation, which multiply quickly in a large-scale breach. Intentional violations can even lead to criminal charges.
The False Claims Act is equally severe, with fines up to three times the program’s loss plus thousands per false claim. Other laws carry their own steep penalties:
- Anti-Kickback Statute: Criminal fines, imprisonment, and exclusion from federal programs.
- EMTALA: Fines up to $133,420 per violation as of December 2024.
- OSHA: Penalties up to $161,323 per violation.
- Sunshine Act: Fines up to $1 million.
Beyond direct fines, the indirect costs include loss of licensure, damaged reputation, and eroded patient trust. The Ponemon Institute reports that while compliance costs an average of $3.5 million annually, non-compliance costs nearly $9.4 million. Investing in a robust compliance program is not just the right thing to do—it’s a smart business decision.
Key Federal Laws Governing Healthcare Compliance
Navigating federal healthcare regulations is complex but essential. These laws are the backbone of compliance for healthcare, designed to protect patients and prevent fraud. The Office of Inspector General (OIG) offers valuable guidance on fraud and abuse laws to help providers. Federal laws set the baseline, but organizations must also adhere to often stricter state laws and local codes.
HIPAA and HITECH: The Foundation of Patient Privacy
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is the cornerstone of patient privacy, establishing national standards for protecting Protected Health Information (PHI).
- The Privacy Rule gives patients rights over their health information and limits its use and disclosure.
- The Security Rule mandates administrative, physical, and technical safeguards for electronic PHI (ePHI).
- The Breach Notification Rule requires notification to individuals and HHS if unsecured PHI is compromised.
The HITECH Act of 2009 strengthened HIPAA enforcement and increased penalties, emphasizing the importance of data protection in the digital age. For more details, the CDC offers helpful resources. More on HIPAA.
Financial Integrity and Anti-Fraud Regulations
These laws ensure healthcare funds are handled ethically.
- The Stark Law (Physician Self-Referral Law) prohibits doctors from referring Medicare/Medicaid patients to entities where they have a financial interest, ensuring decisions are based on patient needs, not profit.
- The Anti-Kickback Statute (AKS) makes it a crime to exchange anything of value for referrals of federal healthcare program business.
- The False Claims Act (FCA) prohibits submitting false claims for payment to programs like Medicare. Its “qui tam” provision allows whistleblowers to sue on behalf of the government. Learn more at the Justice Department’s page on the False Claims Act.
- The Physician Payments Sunshine Act requires manufacturers to report payments to physicians and teaching hospitals, promoting transparency.
Patient Safety and Access to Care Laws
These laws ensure patients receive safe, appropriate care.
- The Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act (EMTALA) requires hospitals to provide a medical screening and stabilizing treatment to anyone seeking emergency care, regardless of their ability to pay. More on EMTALA.
- The Patient Safety and Quality Improvement Act (PSQIA) encourages voluntary, confidential reporting of medical errors to Patient Safety Organizations (PSOs) to improve overall safety.
- The Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) ensures safe working conditions for healthcare employees, which is essential for providing quality patient care.
- Other key laws include the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which reformed healthcare access and quality; the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA), which ensures drug and device safety; and the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA), which protects against discrimination based on genetic information.
Building an Effective Program for Compliance for Healthcare
An effective compliance for healthcare program weaves ethical and legal responsibility into your organization’s culture. The Office of Inspector General (OIG) emphasizes a proactive approach, creating a culture where doing the right thing is standard practice. Our commitment to Compliance and Industry Standards reflects this philosophy.
The 7 Core Elements of a Successful Program
The OIG outlines seven fundamental elements for a successful compliance program:
- Written Policies and Procedures: Create clear, accessible, and regularly updated guidelines that define expected conduct.
- Compliance Officer and Committee: Designate a leader and/or committee with the authority and resources to oversee the program.
- Effective Lines of Communication: Establish safe channels, like a confidential hotline, for employees to report concerns without fear of retaliation.
- Internal Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly conduct audits to identify risks and verify that policies are being followed.
- Well-Publicized Disciplinary Guidelines: Enforce standards consistently and fairly to show that compliance is mandatory.
- Prompt Response and Corrective Action: Investigate detected problems thoroughly and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Ongoing Training and Education: Provide regular, role-specific training to ensure all staff understand their compliance responsibilities. The HHS General Compliance Program Guide offers valuable insights.
The Role of Leadership in Fostering a Compliant Culture
A compliance program cannot succeed without strong leadership. The “tone from the top” is the most critical factor in creating a culture of compliance for healthcare.
Leaders must model ethical behavior, allocate sufficient resources (budget, staff, technology), and champion a “speak-up” culture where employees feel safe reporting concerns. When leadership integrates compliance into strategic planning and daily operations, it sends a clear message that integrity is a non-negotiable priority. As a trusted IT partner for Maryland healthcare organizations, we’ve seen that leadership commitment turns compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage.
Overcoming Common Compliance Challenges with Technology
Even with a solid program, compliance for healthcare presents challenges: ever-changing regulations, tight budgets, legal complexity, and ensuring employee buy-in. However, technology can transform these obstacles into manageable tasks. Smart IT solutions, particularly Cybersecurity for Healthcare Organizations, can make a significant difference.
Many providers are stretched thin, with some relying on a single person or manual processes. This is risky and inefficient, especially when 43% of organizations still use paper for policy management.
Practical Steps to Strengthen Your Compliance for Healthcare Efforts
A strategic, technology-enabled approach can make compliance a proactive process.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Use internal and external audits to find and fix weak spots before regulators do.
- Invest in Role-Based Training: Make training practical and specific to each employee’s job function.
- Foster a “Speak-Up” Culture: Create safe, anonymous channels for employees to report concerns without fear of backlash.
- Automate with Technology: Use technology to automate routine tasks, reduce human error, and free up staff to focus on patient care. Our Data Protection Strategies and Secure IT Infrastructure Best Practices help weave compliance into daily operations.
How Technology and IT Partners Bolster Compliance
Technology is essential for modern compliance for healthcare.
- Compliance Software: These platforms automate policy management, training tracking, risk assessments, and incident reporting.
- Modern EHRs: Today’s Electronic Health Records are built with HIPAA/HITECH requirements in mind, featuring secure data storage, audit trails, and access controls.
- Robust Cybersecurity: Multi-layered security is fundamental. This includes encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular vulnerability assessments to protect PHI from threats like ransomware.
- Managed IT Services: Partners like us can take the burden off your team. Our Managed IT Services for Healthcare provide expert support to keep your systems secure, updated, and compliant.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: HIPAA requires contingency plans. Our Data Backup and Disaster Recovery for Healthcare solutions ensure PHI is protected and available.
- Secure Cloud Solutions: Our Cloud Computing for Healthcare services help organizations leverage the cloud safely and compliantly.
Looking ahead, trends like telehealth, AI governance, and stricter cybersecurity rules will continue to shape compliance. Working with an experienced IT partner like Alliance InfoSystems provides the expertise to steer these complexities, so you can focus on patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions about Healthcare Compliance
We hear these questions all the time from healthcare providers. Here are straightforward answers to common concerns about compliance for healthcare.
What is the single most important healthcare compliance law?
While all laws work together, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is foundational. It governs the privacy and security of all patient health information, touching nearly every aspect of healthcare operations and forming the bedrock of patient trust. However, a truly compliant organization must also respect other critical laws like the Stark Law, Anti-Kickback Statute, and EMTALA.
Who is responsible for compliance in a healthcare organization?
Everyone is responsible. While a Compliance Officer and leadership team create the framework, every employee—from clinicians to administrative staff—plays a critical role. Compliance is a team sport, and this shared responsibility makes an organization more resilient and trustworthy.
How can a small practice manage healthcare compliance with limited resources?
Small practices can manage compliance effectively by being strategic.
- Start with a risk assessment to focus resources on the highest-priority areas.
- Leverage technology to automate tasks and use EHRs with built-in compliance features.
- Partner with external experts like IT providers or consultants for specialized knowledge without the cost of full-time staff.
- Prioritize role-specific training for your staff, as they are your first line of defense.
Investing smartly in compliance is more cost-effective than facing the potentially devastating penalties of non-compliance.
Conclusion: Fostering a Lasting Culture of Compliance
It’s clear that compliance for healthcare is more than a checklist; it’s a fundamental commitment to patient safety, data privacy, and ethical operations. Adhering to standards like HIPAA and anti-fraud laws isn’t just a legal requirement—it’s a promise to your patients and community.
This journey requires constant attention and a culture of integrity, starting with strong leadership and involving every team member. While avoiding steep penalties is a motivator, the real rewards are priceless: deep patient trust, a strong reputation, and smoother operations.
In today’s world of evolving regulations and cyber threats, technology is an essential ally. Smart software and robust cybersecurity are critical for managing the complexities of modern compliance for healthcare. For Maryland-based healthcare organizations, navigating this landscape can be a full-time job.
That’s where a trusted partner like Alliance InfoSystems comes in. With over 20 years of experience, we specialize in managing the technical side of data security and compliance. We offer customized, budget-friendly solutions to keep your systems secure, updated, and aligned with regulatory requirements.
Ready to strengthen your organization’s security and ensure robust compliance for healthcare? Explore our comprehensive Managed Security Services today. We’re here to help you every step of the way!