Minimize data loss: Ultimate Security 2025
Why Minimizing Data Loss is Non-Negotiable
For any business, the ability to minimize data loss is crucial for survival. It means protecting vital information from being lost or becoming unusable.
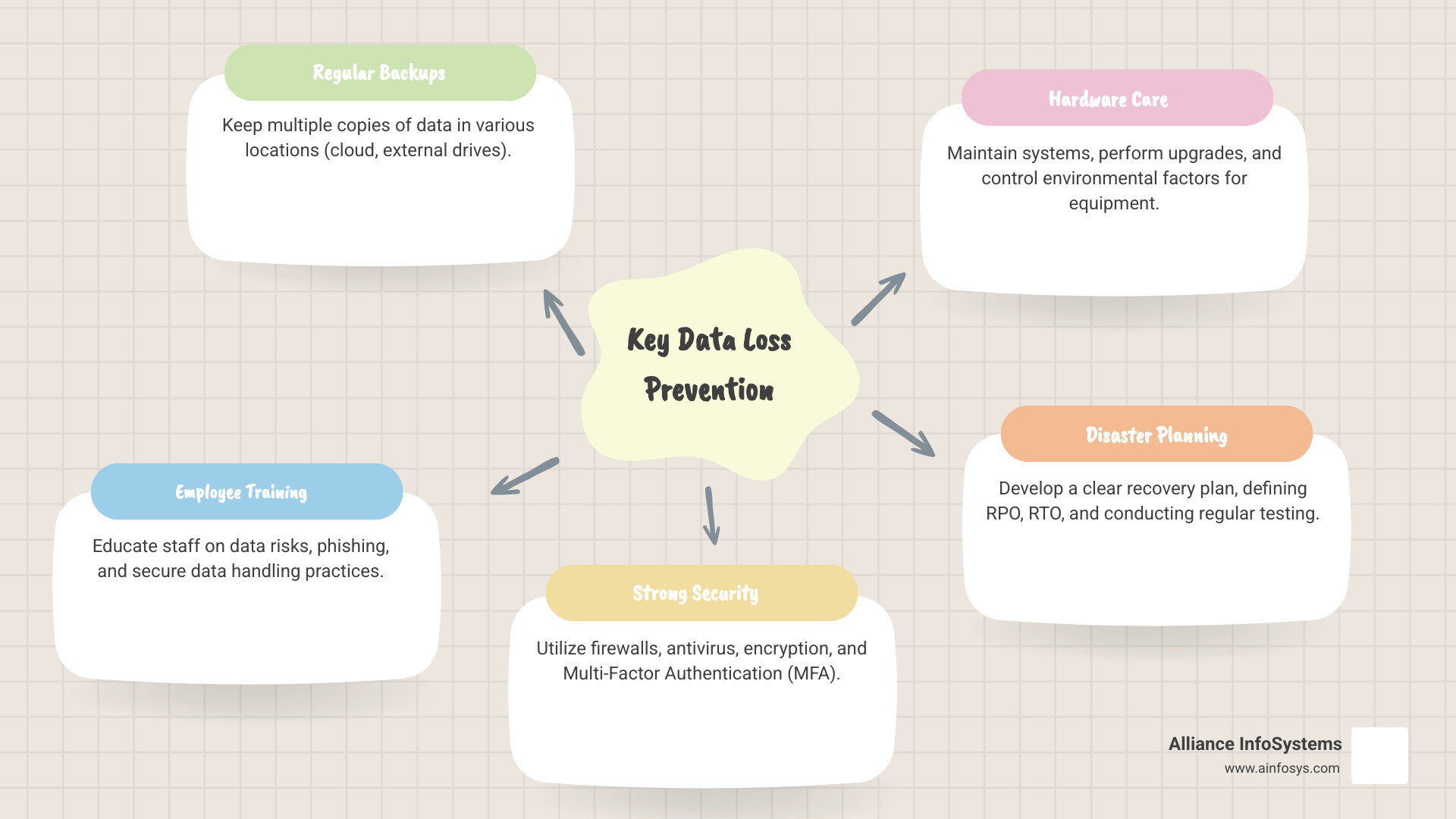
If you’re looking for the quickest ways to prevent data loss, here are the core strategies:
- Regular Backups: Keep copies of your data in multiple places.
- Employee Training: Teach staff about data risks and safe practices.
- Strong Security: Use firewalls, antivirus, and encryption.
- Hardware Care: Maintain your systems and replace old equipment.
- Disaster Planning: Have a clear plan for what to do if data is lost.
Data loss occurs when important information is deleted, corrupted, or made inaccessible. This can range from a single file to a system-wide crash, affecting businesses of all sizes.
When data disappears, the impact is severe: costly downtime, lost sales, and reputational damage. The cost of data loss exceeds $75 billion annually in downtime for small companies, and 40-60% of small businesses never reopen after a major data disaster.
This guide covers the essential steps to protect your data, from common causes to best practices. Our goal is to help you build a resilient defense against data loss and keep your business running smoothly.
Understanding the Enemy: Common Causes of Data Loss
To minimize data loss, we must first understand the threats. Data loss can manifest in various ways, each representing a different risk to your valuable information. Let’s examine the most common culprits:
- Human Error: Simple mistakes like accidental deletion or mishandling information are a leading cause of data loss. While not always malicious, the impact can be devastating.
- Hardware Failure: Computers, servers, and hard drives don’t last forever. Mechanical failures are a real threat and can happen without warning, taking your data with them.
- Software Corruption: Bugs, failed updates, or software conflicts can scramble data, making it unreadable and causing unexpected downtime.
- Power Outages and Natural Disasters: Power surges can corrupt files and damage hardware. Natural disasters like floods or fires can wipe out physical IT infrastructure. As highlighted in The Uptime Institute’s annual outage analysis report, power issues are a significant threat to data centers.
- Malware and Ransomware: These malicious programs are designed to steal, corrupt, or lock up your data, often demanding a ransom. They are a huge concern for all businesses.
- Device Theft: Losing a laptop, smartphone, or external hard drive means the data on it is gone, especially if unencrypted. Physical security is as important as digital.
- Malicious Insiders: A disgruntled employee or contractor might intentionally delete or steal data. It’s a tough reality every business must consider.
Understanding these threats is the first step toward building a strong defense to minimize data loss.
The Human Element in Data Breaches
People are often the weakest link in data security. Our actions, or inactions, contribute significantly to data loss, from accidental deletion to formatting the wrong drive.
Human error also includes security lapses leading to data breaches. Phishing attacks trick employees into revealing credentials, which can be compromised in a moment of distraction.
Misconfigured cloud services are another major risk. A simple oversight in settings can expose sensitive data to the internet with massive consequences.
Poor security hygiene, like using weak passwords or sharing logins, is a common problem. A general lack of training leaves employees vulnerable. As the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) highlights, the human element is involved in a vast majority of incidents, making team training paramount.
Hardware and System Failures
Hardware isn’t indestructible. Components like hard drives have a limited lifespan and are prone to failure. Servers can also malfunction, leading to system crashes and inaccessible data.
External factors also affect hardware health. Power surges can cause immediate damage, while environmental factors like heat and humidity degrade performance over time. Unpatched systems create vulnerabilities that lead to instability and data loss. Regular maintenance and updates are crucial.
Foundational Strategies for Data Protection
To minimize data loss, you need a proactive, foundational approach focused on data integrity. This ensures your data is reliable, accurate, and unaltered throughout its lifecycle, preventing compliance issues and business problems.
Key foundational strategies include:
- Data Classification: Sorting data into categories (e.g., “public,” “internal,” “highly confidential”) to apply the appropriate level of protection.
- Access Control Policies: Setting clear rules so only authorized individuals can access specific data.
- Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): Giving users and systems only the minimum access required to perform their jobs, reducing potential damage from a compromised account.
- Developing a Data Management Plan: Creating a clear roadmap that outlines how data is stored, accessed, retained, and backed up.
Best practices for data integrity include:
- Ensuring systems meet industry regulations.
- Following a solid SDLC for custom software.
- Validating computer systems to ensure they work as intended.
- Implementing detailed audit trails to track data access and changes.
- Using software to detect and correct data errors proactively.
- Securing records by enforcing the principle of least privilege.
- Maintaining and regularly testing comprehensive backup and recovery plans.
- Designing a QMS with clear SOPs for data-related tasks.
- Protecting the physical and digital security of all systems.
- Establishing a vendor management program for third parties.
- Training staff on safe data handling and maintaining training records.
- Conducting regular internal audits to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Compliance
Data integrity is crucial for regulatory compliance. Industries like pharmaceuticals follow principles such as ALCOA (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate), as detailed in the FDA’s guidance on data integrity. Regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS also have strict data protection rules.
Robust audit trails provide a detailed history of data activity, while system validation ensures systems perform correctly. These steps are vital for smooth operations, passing audits, and avoiding fines.
Key Strategies to Minimize Data Loss from Hardware Failure
Hardware inevitably fails, but that doesn’t have to mean data catastrophe. Several smart steps can minimize data loss from hardware failure:
- Proactive Hardware Replacement: We monitor hardware age and performance, replacing components like hard drives and servers before they fail, typically around the five-year mark as manufacturers suggest.
- Environmental Monitoring: We use controls and sensors in server rooms to maintain optimal temperature and humidity and to detect threats like power spikes or water leaks before they cause damage.
- Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID): We spread data across multiple hard drives. If one fails, the data can be rebuilt from the others, preventing immediate loss and allowing time for replacement.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): A UPS provides battery backup during a power outage, allowing systems to shut down gracefully and preventing data corruption from sudden power loss.
The Ultimate Safety Net: Robust Backup and Disaster Recovery
Even with the best preventative measures, data loss can still happen. A robust backup and disaster recovery strategy is the ultimate safety net, enabling quick and efficient restoration of operations after an incident.
A cornerstone of our strategy is the 3-2-1 backup rule:
- 3 copies of your data: This includes your primary data and two backups.
- 2 different media types: Store your backups on at least two different types of storage (e.g., internal hard drive and cloud storage).
- 1 offsite copy: Keep at least one backup copy in a separate geographic location.
Recovery planning focuses on two key metrics: Recovery Point Objective (RPO), the maximum acceptable data loss, and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), the maximum tolerable downtime. These objectives guide backup frequency and recovery speed and are integral to a Business Continuity Plan (BCP).
Choosing the Right Backup Method
We use a mix of backup methods for comprehensive protection:
| Backup Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | All selected data is copied every time. | Simplest to restore (single set of data). | Time-consuming, requires significant storage space. |
| Incremental | Only data that has changed since the last backup (full or incremental) is copied. | Fastest backup time, uses least storage. | Restoration can be complex, requiring the last full backup plus all incrementals. |
| Differential | Only data that has changed since the last full backup is copied. | Faster than full backup, simpler restoration than incremental (last full + one differential). | Requires more storage and time than incremental over time. |
Storage locations are also key: On-site backups for speed, cloud backups for disaster resilience, and hybrid cloud backups for the best of both. We also use image-based backups for full system recovery (bare-metal recovery) and virtualization for recovery, which boots backups as virtual machines to minimize downtime.
The Importance of Testing and Verification
A backup that can’t be restored is useless. Testing and verification are non-negotiable.
- Automated Backup Testing: We use tools to automatically test backup integrity and bootability, catching issues before a disaster.
- Recovery Drills: We regularly conduct simulated data loss scenarios to practice restoration procedures, identify weaknesses, and improve team proficiency.
- Disaster Recovery Simulations: We perform full-scale simulations to test the entire BCP, including failover processes and communication protocols.
These tests ensure recoverability and data protection. To learn more about developing a robust strategy, you can find more info about data backup and recovery services on our website.
Technological and Human Defenses to Minimize Data Loss
Protecting data requires multiple layers of defense, combining smart technology with well-informed people to create a powerful shield and minimize data loss.
We use a layered security approach, like multiple locks on a door. Each layer—firewalls, encryption, monitoring—works together to protect information across your network, devices, and applications.
A key tool is Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software. It acts like a digital bouncer, designed to detect, block, and report unauthorized attempts to move sensitive data. DLP monitors data in motion (networks), at rest (storage), and in use (endpoints).
Encryption is another vital layer. We encrypt data both at-rest (stored) and in-transit (moving across networks). This makes data unreadable and useless to unauthorized users. We use industry standards like 256-bit AES.
Firewalls and antivirus software are everyday heroes. Firewalls block malicious network traffic, while antivirus programs scan for and eliminate malware. We keep these systems constantly updated against new threats.
For personal security, we use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). It requires two or more forms of verification (e.g., password and a phone code), making it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access, even with a stolen password.
How Employee Training Helps Minimize Data Loss
Technology has a weak spot: people. Human error is a major cause of data loss, making employees the first line of defense. We invest heavily in training and awareness programs.
Our ongoing cybersecurity awareness programs teach employees about online threats and smart habits, like using strong, unique passwords and securing personal devices used for work.
We train our team to recognize phishing and social engineering attacks. Learning to spot fake emails and suspicious requests makes employees a much harder target for criminals.
Clear secure data handling policies provide a guide for storing, sharing, and managing sensitive data. This includes using approved storage and avoiding public Wi-Fi for work. This is crucial because, as Gartner points out, through 2025, 99% of cloud security failures will likely stem from human error, making safe cloud usage a key training topic.
Finally, we foster a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting security incidents immediately. Early detection is key to a fast response, which can dramatically minimize data loss.
Frequently Asked Questions about Preventing Data Loss
Here are answers to common questions about how to minimize data loss.
What is the most common cause of data loss?
Human error is the leading cause of data loss. This includes accidental deletion, overwriting data, or falling for phishing scams. These simple mistakes can have major consequences.
However, hardware failure is also a major factor, as components have a limited lifespan. Cyberattacks like ransomware are another constant threat designed to steal or corrupt your data. While human error is number one, hardware failure and cyberattacks are close behind.
What is the difference between data loss and a data breach?
These terms are often confused but describe different events.
Data loss is when data is destroyed or becomes unusable, affecting its availability and integrity. A crashed hard drive causing files to disappear is an example of data loss.
A data breach is a security incident where an unauthorized party accesses sensitive data, compromising its confidentiality. For example, a hacker stealing a customer email list is a data breach. The data still exists but is now in the wrong hands.
A breach can lead to data loss (e.g., a hacker deletes data after stealing it), but they are distinct issues. Not all data loss involves a breach, and not all breaches cause data loss.
How often should I back up my data?
The ideal backup frequency depends on your Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—the maximum amount of data your business can afford to lose.
For critical systems, like those handling financial transactions, continuous backups or snapshots every few minutes may be necessary, as losing even a moment of data is disastrous.
For less critical data, daily or weekly backups might suffice. The more frequently you back up, the less data you risk losing. It’s about balancing your business needs with the cost and effort of backups.
Conclusion
We’ve covered the many challenges to data safety, from human error to hardware failure and cyberattacks. The good news is you are now armed with the knowledge to tackle them.
The ability to minimize data loss is a fundamental pillar of business success. We’ve seen how foundational strategies, robust backup plans, and a mix of technology and trained staff create a resilient data environment.
This requires a shift from a reactive to a proactive mindset: constantly monitoring, testing defenses, empowering your team, and adapting your strategies as your business evolves.
You don’t have to take this journey alone. As a Maryland-based IT services company with over 20 years of experience, Alliance InfoSystems understands the challenges your business faces. We are your reliable IT partner, crafting flexible, customized, and cost-efficient services to fit your needs. We handle the complexities of data security so you can focus on growing your business.
Don’t wait for a crisis. Let’s work together to build your defense. Develop your data backup and recovery plan today, and let us help ensure your business stays productive, protected, and prepared for anything!